AGRICULTURAL NUTRIENT PROFILE: PHOSPHORUS-PART 1
The importance of phosphorus to crops
Phosphorus (P) takes its rightful place alongside Nitrogen and Potassium among the three primary macronutrients essential to successful plant growth.
Without Phosphorus, photosynthesis could not occur. Phosphorus plays a key role in complex energy transformations that are necessary to all life, as a main ingredient in ATP (adenosine triphosphate). It is also a central component of DNA and RNA – and is necessary for building proteins and other compounds.
That is just the beginning. Phosphorus is required by the plant from the seedling stage through to maturity – and has a measurable impact on crop quality and yield.
Ten ways phosphorus aids in plant growth and plant health:
- Enables photosynthesis (energy transformation)
- Builds nucleic acids, proteins and enzyme
- Facilitates root growth
- Strengthens stems and stalks
- Improves flower formation and seed production
- Promotes crop uniformity
- Contributes to earlier maturity
- Increases disease resistance
- Improves overall crop quality
- Facilitates nitrogen fixation abilities of legumes
Identifying phosphorus deficiency
As you can see, the importance of phosphorus to crops cannot be understated. It explains why a Phosphorus deficiency can have a devastating impact on crop quality and yield.
Plants suffering from phosphorus deficiency show several telltale signs: such as stunted growth and fibre colours ranging from dark green to reddish purple (caused by the accumulation of sugars). Phosphorus deficiencies later in the growing season will negatively affect seed and fruit development, as well as crop maturity.
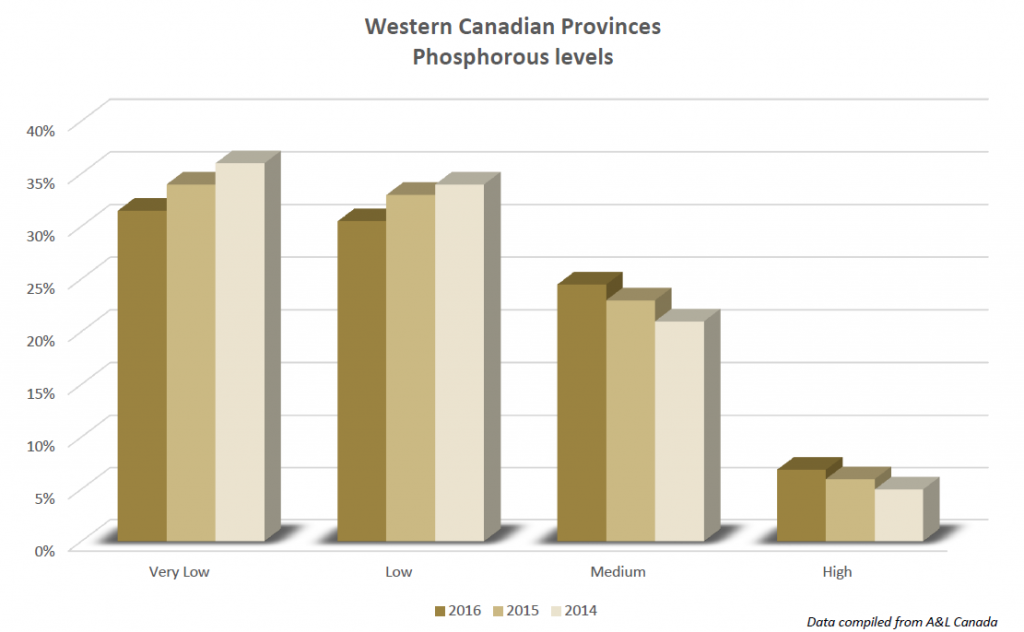
A&L Canada Laboratories has been compiling results from soil tests across western Canada. As the chart below demonstrates, the majority of tests indicate low or very low Phosphorus levels across the prairie provinces, based on a fairly substantial sampling size.
It is important to be proactive in ensuring your plants have an adequate supply of P – because if you wait until you see signs of deficiency, the damage has already been done.
Fortunately, growers have several tools to help determine phosphorus levels in the soil. Various soil tests can be used to determine phosphorus availability in the soil.
As well, a Nutrient Uptake and Removal Chart can help growers determine how much phosphorus a crop will require, and how much it will consume.
Phosphorus Facts
Did you know…
- The total Phosphorus content in surface soils is very low: only 0.6% on average (compared to 0.14% for Nitrogen and 0.83% for Potassium).[1]
- Only 10% to 30% of a crop’s Phosphorus requirements come from fertilizers. The remainder comes from the native soil.[2]
[1] http://www.cropnutrition.com/efu-phosphorus
[2] The Agronomy Handbook, Midwest Laboratories. Editors: Don Ankerman, B.S., Richard Large, Ph.D. Page 25.